Everything you need to know about GSLV Mk III

The upper stage of GSLV MkIII vehicle is a new cryogenic stage (C25) indigenously configured, designed and realised by ISRO.

Pic credit: ISRO website
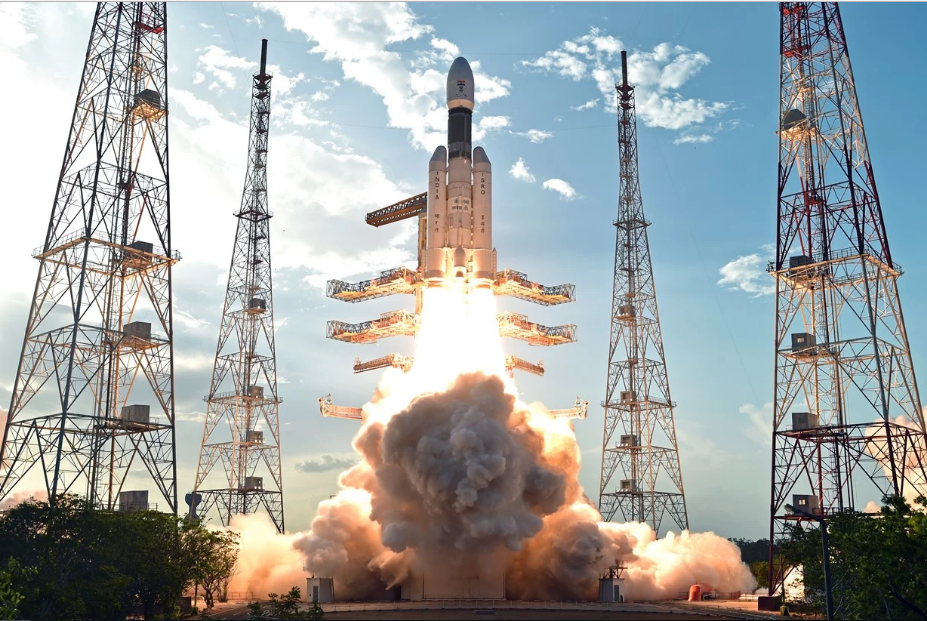
The Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) on June 5 launched India’s heaviest rocket Geosynchronous Satellite Launch Vehicle-Mark III (GSLV Mk III) from Sriharikota.
“The first developmental flight (GSLV MkIII-D1) of India’s heavy lift launch vehicle GSLV Mk-III was successfully conducted today (June 05, 2017) evening from Satish Dhawan Space Centre SHAR, Sriharikota with the launch of GSAT-19 satellite,” said ISRO in its press statement after the launch.
Here is everything you need to know about ISRO and India’s new achievement:
1. The height of GSLV Mark III is 43.43 metres. It weighs 640 tons.
2. This was the first orbital mission of GSLV MkIII which was mainly intended to evaluate the vehicle performance including that of its fully indigenous cryogenic upper stage during the flight, said ISRO.
3. GSAT-19 is billed as the heaviest satellite launched from the Indian soil. It weighed 3136 kg at lift-off.
4. After a twenty-five-and-a-half hour smooth countdown, the mission began with the launch of GSLV Mk-III at 5:28 pm IST from the Second Launch Pad as scheduled with the ignition of its two S200 solid strap-on boosters.
5. Then the major phases of the flight occurred as scheduled.
6. The upper stage of GSLV MkIII vehicle is a new cryogenic stage (C25) indigenously configured, designed and realised by ISRO, said the organization.
7. The cryogenic stage used liquid Hydrogen and liquid Oxygen as propellants with a total loading of 28 tons.
8. The stage is powered by a 20 ton thrust cryogenic engine (CE20) operating on ‘gas generator cycle’.
——————————————
You may like to read
9. The ISRO confirmed that the performance of the engine and stage during the mission was as predicted.
10. About 16 minutes after lift-off, GSAT-19 satellite was successfully placed in orbit.
11. Soon after its separation from GSLV, the Master Control Facility (MCF) at Hassan in Karnataka took control of the satellite. GSAT-19 is a high throughput communication satellite.
12. The ISRO said that in the coming days, GSAT-19 orbit will be raised from its present Geosynchronous Transfer Orbit (GTO) to the final circular Geostationary Orbit (GSO) by firing the satellite’s Liquid Apogee Motor (LAM) in stages.
13. During the final phase of this operation, the solar panels and antenna reflectors of the satellite will be deployed.
14. The satellite will be commissioned into service after its positioning in the designated slot in the GSO following in-orbit testing of its payloads.
Big Wire